An uninterruptible power supply (UPS), or uninterruptible power source, is an electrical device that provides emergency power to a load when the input power source or main power fails. It can also condition incoming power to prevent sensitive electronic equipment from being damaged by all-too-common sags and surges. Read More…
TDK-Lambda Americas designs and manufactures a wide range of AC-DC and DC-DC power supplies and EMI Filters for Medical, Telecom, Industrial, Datacom, and Test & Measurement applications worldwide. The company has been a major provider of power solutions since 1948. TDK-Lambda is a subsidiary of the TDK Corporation, a leading global electronics company.

Our company offers a variety of standard and custom power supplies. These items are great for a wide range of applications. If you have any special requests then please let our representatives know. If you ever run into any questions or issues then our engineers are available to assist you. There is no project too challenging for our teams! Give us a call today!

For 4 decades, Acopian Power Supplies has specialized in long lasting power supplies (0 volts – 30000 V). We offer AC power supplies, DC power supplies, AC to DC converters, uninterruptible power supply (UPS), AC to DC power supplies & high voltage power supplies. With quality customer service & technical support, we have thousands of power supplies for thousands of applications.
APS are specialists in power conversion and the manufacture of high performance power systems. Products include power converters and inverters; motor drives and brakes; battery chargers; AC and DC power supplies; driver circuits and more. Custom and standard power systems are available.
At Quail Electronics, we are your power cord specialists. Our power supplies consist of green dot cords, high voltage cords, North American and international cords, specialty cords, plus adapters, plugs and strips.

More Uninterruptible Power Supply Manufacturers
Comprehensive Guide to Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): Types, Applications, and Buying Considerations
Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) are critical for protecting sensitive electronics and IT infrastructure from power surges, outages, voltage fluctuations, and other electrical anomalies. Whether you’re safeguarding data centers, medical equipment, industrial automation, or home office computers, selecting the right UPS system is essential for ensuring uptime, data integrity, and overall business continuity. This guide explores the different types of UPS technology, their unique benefits and applications, and key decision factors to help you choose the best UPS solution for your specific requirements.
Types of Uninterruptible Power Supplies
There are several main types of UPS systems, each designed to address specific power protection needs and operational environments. Understanding the core differences between these uninterruptible power supply technologies can help you determine which is right for your application.
Single Conversion UPS System
Single conversion UPS, often referred to as offline UPS or standby UPS, feeds incoming utility AC power directly to connected devices during normal operation. When the AC input supply falls outside of preset limitations (due to a blackout, brownout, or spike), the UPS seamlessly switches to battery backup, isolating the load from unstable utility power. During this transition, the UPS disconnects the AC input to prevent backfeed from the inverter to the utility grid.
This topology is commonly found in residential, small office, and entry-level IT applications where cost-efficiency and basic protection against short-term power interruptions are priorities. Standby and line-interactive are two prevalent single-conversion UPS designs.
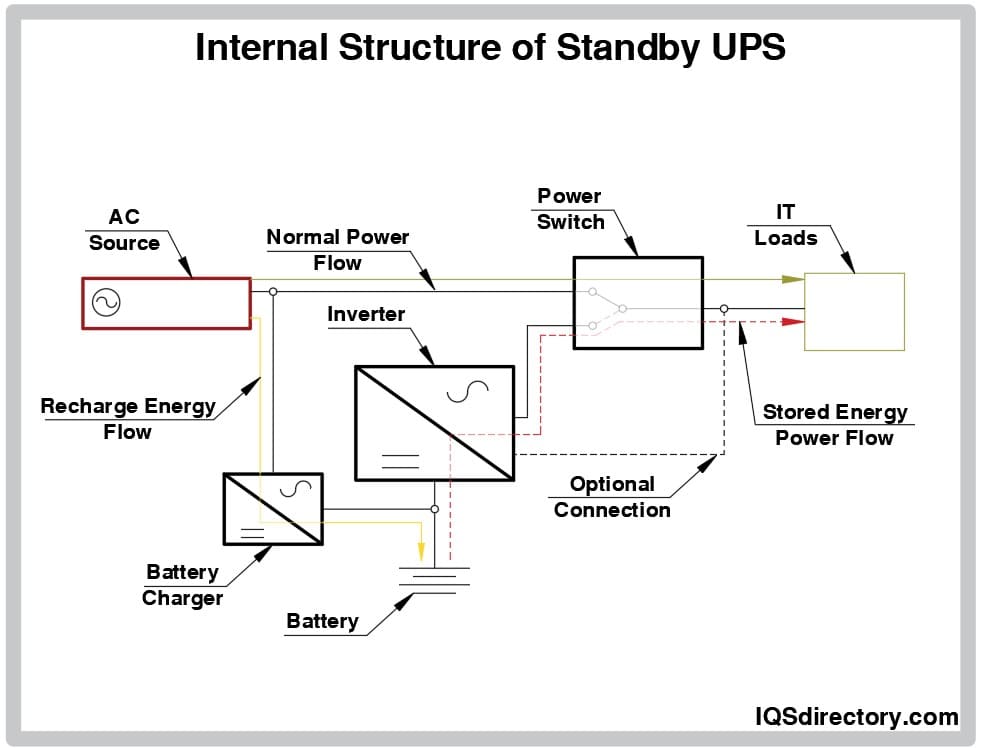
Standby UPS
A standby UPS (sometimes called an offline UPS) allows IT equipment and other sensitive electronics to operate on utility power under normal circumstances. When a voltage irregularity or power failure is detected, the UPS quickly switches to battery power to keep your devices running. Some standby UPS designs include transformers or filters to provide limited power conditioning, helping to smooth out minor sags or surges.
- Ideal for desktop computers, point-of-sale (POS) systems, and home electronics
- Economical solution for non-critical loads
- Short transfer time between utility and battery power
Line Interactive UPS System
Line-interactive UPS systems incorporate advanced technology to regulate minor fluctuations in input voltage—such as brownouts (undervoltage) and power swells (overvoltage)—without the need to switch to battery mode. This is achieved via an autotransformer that can boost or reduce voltage as needed, providing superior power conditioning and extended battery life compared to basic standby UPS units.
- Recommended for small business servers, network switches, and entry-level storage devices
- Offers improved voltage regulation and surge protection
- Minimizes unnecessary battery usage for longer lifespan
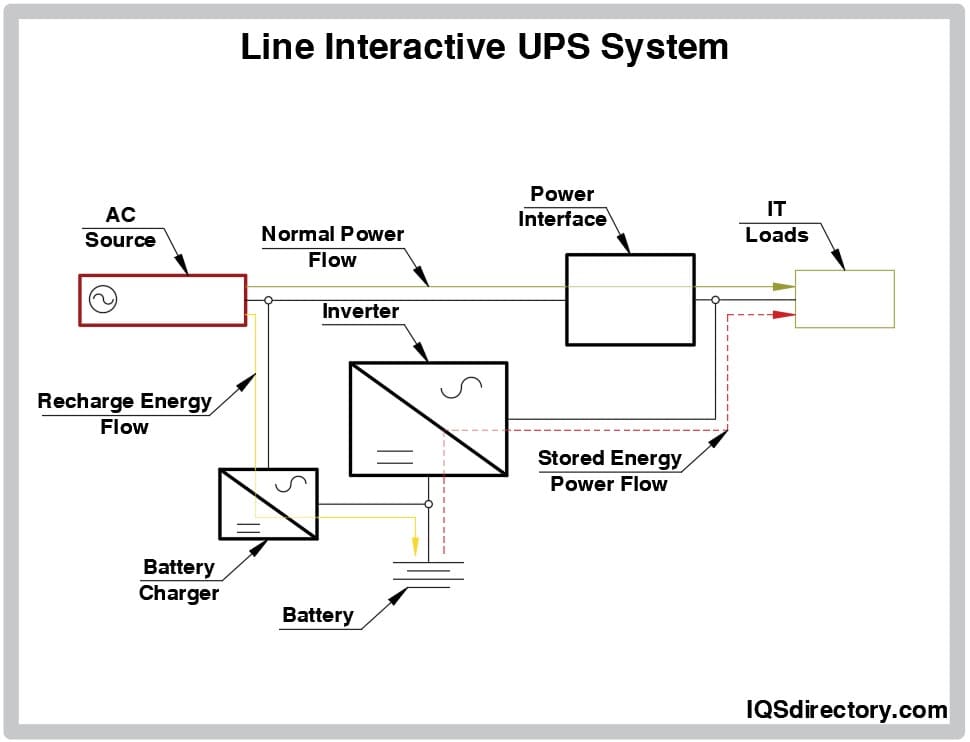
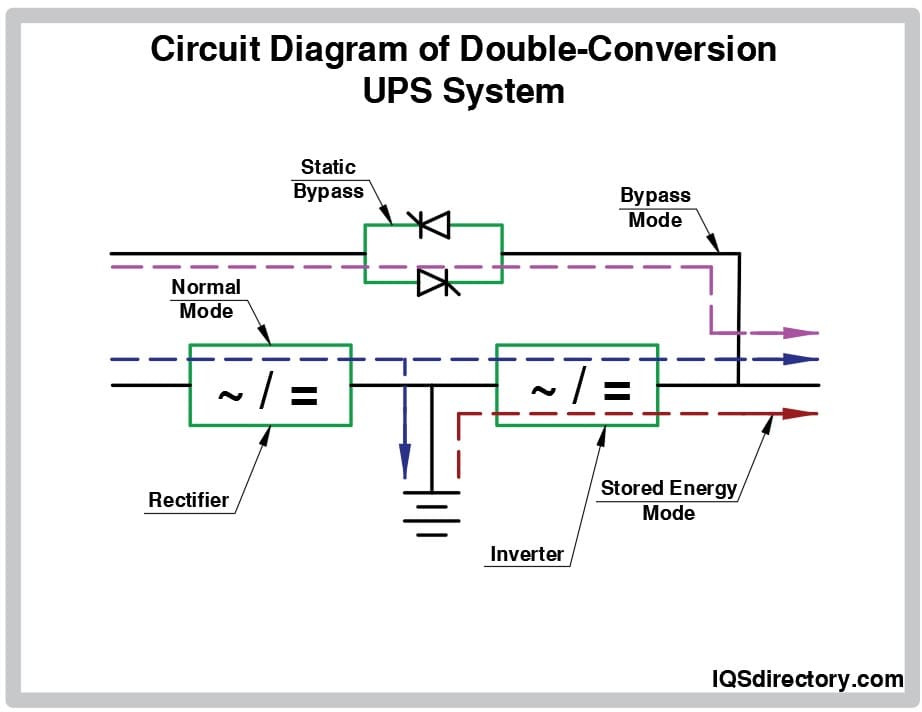
Double-Conversion UPS System (Online UPS)
The double-conversion UPS, also known as an online UPS, provides the highest level of power protection. It continuously converts incoming AC power to DC through a rectifier, and then inverts it back to clean, stable AC output. This dual process isolates connected equipment from fluctuations, spikes, electrical noise, and outages, ensuring mission-critical devices always receive reliable power.
Online UPS systems are widely used in data centers, healthcare, financial services, telecom infrastructure, and other environments where even a brief disruption can lead to data loss, equipment damage, or costly downtime. If the AC input supply falls outside of acceptable parameters, the input rectifier disengages and the UPS draws power from the battery—without any transfer time.
- Provides seamless, uninterrupted power for critical loads
- Completely isolates equipment from unstable utility power
- Includes bypass circuits for fault tolerance and maintenance
- Essential for high-availability and zero-downtime applications
Multi-Mode (Hybrid) UPS Systems
Multi-mode or hybrid UPS systems combine the efficiency of line-interactive topology with the robust protection of double-conversion UPS. These advanced units automatically select the optimal operating mode based on real-time power conditions, maximizing energy efficiency during normal operation and switching to online mode when disturbances are detected.
- Best suited for enterprises seeking both high efficiency and superior power quality
- Reduces total cost of ownership by optimizing power usage
- Flexible for a wide range of commercial and industrial applications
Common Applications and Use Cases for UPS Systems
UPS solutions are deployed across various sectors to protect hardware and maintain operational continuity. Choosing the right UPS model depends on your environment, equipment sensitivity, and business objectives. Below are some of the most common use cases and industries that benefit from dependable uninterruptible power supply systems:
- Data Centers: Continuous operation of servers, storage, and networking infrastructure; supports failover and disaster recovery strategies.
- Healthcare Facilities: Ensures medical devices, diagnostic equipment, and life-support systems remain powered during outages.
- Industrial Automation: Protects PLCs, robotics, manufacturing lines, and process control systems from voltage disturbances.
- Telecommunications: Maintains uptime for mission-critical communication equipment and broadband networks.
- Financial Services: Prevents transaction disruptions and data loss in banking, trading floors, and payment processing centers.
- Retail and Point-of-Sale: Keeps POS terminals, barcode scanners, and security systems online during utility failures.
- Education and Research: Safeguards laboratory instruments, e-learning platforms, and IT labs.
- Home Office and Small Business: Provides reliable backup for computers, routers, and smart devices.
Benefits of Using Uninterruptible Power Supplies
Investing in a UPS system offers multiple advantages for both businesses and individuals:
- Prevents Data Loss: Ensures critical files and databases remain accessible, even during sudden outages.
- Protects Equipment: Shields electronics from surges, sags, and voltage spikes that can cause hardware failure.
- Guarantees Business Continuity: Minimizes downtime, supports remote work, and helps meet regulatory compliance requirements.
- Facilitates Safe Shutdown: Allows time for proper system shutdown or failover to backup generators.
- Improves Power Quality: Filters out electrical noise and provides stable voltage for sensitive devices.
- Reduces Maintenance Costs: Extends equipment lifespan by preventing damage caused by irregular power supply.
Considerations When Choosing a UPS
When selecting a UPS for your specific needs, consider these important factors to ensure optimal protection and value:
UPS Topology
Single-conversion UPSs are typically more energy-efficient and cost-effective, making them suitable for loads with higher failure tolerance. However, they offer less comprehensive protection compared to double-conversion or online UPS systems. Standby UPSs are ideal for small-scale applications (such as desktop computers and POS systems), while line-interactive UPSs are best for entry-level servers, network appliances, and storage devices in environments with stable power.
Double-conversion UPSs, while less energy-efficient, are the preferred choice for mission-critical systems and sensitive electronics that demand uninterrupted, high-quality power. Multi-mode UPSs, although more expensive, offer the best blend of efficiency and protection—making them ideal for enterprise-grade environments where downtime is not an option.
Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase Power
UPS systems are available in both single-phase and three-phase configurations. The choice depends largely on your facility’s power infrastructure and load requirements:
- Single-Phase UPS: Suitable for homes, small businesses, and branch offices with lower power demands (typically less than 20,000 VA).
- Three-Phase UPS: Designed for large data centers, multi-story commercial buildings, and industrial facilities requiring high compute density and long-distance power distribution.
Three-phase power is generated by utilities for commercial and industrial customers, delivering more energy via three independent "phase" wires. In contrast, residential users typically receive single-phase power from the grid.
Capacity and Runtime
Assess the total load (in watts or VA) that your UPS must support. Consider both current requirements and potential future expansion. Also, determine the desired runtime—how long you need backup power during an outage—to ensure critical systems have enough time for safe shutdown or transfer to generator power.
Form Factor and Installation Environment
UPS devices come in various form factors, including tower, rackmount, modular, and compact models. Choose a unit that fits your available space and cooling requirements. For example, rackmount UPS systems are ideal for data centers and server rooms, while compact tower models suit desktops and branch offices.
Battery Type and Maintenance
Most UPS systems use sealed lead-acid (VRLA) batteries, but lithium-ion battery UPS solutions are becoming more popular due to their longer lifespan, lighter weight, and lower maintenance requirements. Consider ease of battery replacement, hot-swappable battery options, and monitoring features to minimize downtime.
Scalability and Redundancy
For growing organizations, look for modular or scalable UPS systems that allow you to increase capacity as needed. Redundant UPS configurations (such as N+1 designs) provide additional fault tolerance, ensuring uninterrupted operation even if one module fails.
Management, Monitoring, and Alarms
Advanced UPS models offer network connectivity, remote management interfaces, and real-time monitoring to notify you of power events, battery status, and environmental conditions. Integration with building management systems (BMS) and automation platforms can streamline maintenance and compliance reporting.
Certifications and Compliance
Depending on your industry, you may require UPS systems that meet specific safety, environmental, and performance certifications (such as UL, CE, RoHS, ISO 9001, or ENERGY STAR). Verify that your chosen UPS meets all relevant regulatory standards.
Budget and Total Cost of Ownership
Balance initial purchase price with long-term costs, including energy consumption, battery replacements, maintenance, and potential downtime. Investing in a high-quality, reliable UPS can result in lower total cost of ownership and improved ROI over time.
How to Select the Right Uninterruptible Power Supplies Manufacturer
Choosing a reputable UPS manufacturer is crucial for receiving high-quality products, expert support, and reliable after-sales service. Here’s how to make an informed decision when buying uninterruptible power supplies:
- Compare Multiple UPS Suppliers: Use our Uninterruptible Power Supplies directory to compare at least 5 manufacturers. Evaluate their product ranges, areas of expertise, and customer reviews.
- Review Company Profiles: Each UPS manufacturer listed has a detailed business profile highlighting experience, capabilities, certifications, and specializations.
- Request Information or Quotes: Use the contact forms provided to ask about specific models, customization options, lead times, and after-sales support.
- Preview Manufacturer Websites: Utilize our proprietary website previewer to get a sense of each company’s strengths and product focus.
- Streamline Your Search: Submit a single RFQ form to contact multiple suppliers with the same requirements, saving time and effort.
Looking for guidance on which UPS brand best fits your business? Ask us about:
- What are the best UPS systems for medical or laboratory applications?
- How do I calculate the correct UPS size for my network or data center?
- Which UPS battery technology is most cost-effective in the long term?
- What are the most reliable UPS manufacturers for industrial or commercial use?
- How can UPS monitoring software improve my facility’s uptime?
Frequently Asked Questions About Uninterruptible Power Supplies
What size UPS do I need for my equipment?
To determine the correct UPS size, add up the total wattage of all devices you plan to protect. Choose a UPS with a capacity (VA rating) at least 20–30% higher than your calculated load to accommodate surges and future expansion. Use our UPS sizing calculator for tailored recommendations.
How long will a UPS run my equipment during a power outage?
Runtime depends on the UPS battery capacity and the total wattage of the protected equipment. Smaller units may offer 5–15 minutes of backup, while larger enterprise models can provide hours of runtime or integrate with external battery packs for extended operation. Consult product datasheets or speak with a manufacturer for precise estimates.
Can I use a UPS with sensitive electronics like medical equipment?
Yes. For sensitive or mission-critical applications, an online (double-conversion) UPS is recommended. These systems provide clean, regulated power and zero transfer time, making them ideal for medical, laboratory, and telecom devices.
Should I choose lead-acid or lithium-ion batteries for my UPS?
Lead-acid (VRLA) batteries are cost-effective and widely available, but require regular maintenance and periodic replacement. Lithium-ion batteries offer longer life, lighter weight, faster recharge, and lower maintenance, but come at a higher upfront cost. Consider your performance, budget, and maintenance requirements when selecting a battery type.
How can I tell when my UPS needs maintenance or battery replacement?
Modern UPS systems feature monitoring software, self-test routines, and alarms to notify you of battery health, impending failures, or service needs. Regularly test your UPS and follow manufacturer guidelines for maintenance intervals.
Next Steps: Find the Best UPS for Your Needs
Ready to protect your business with an advanced UPS solution? Browse our Uninterruptible Power Supplies directory for trusted manufacturers, in-depth product comparisons, and expert buying guides. Whether you’re equipping a mission-critical data center, small business, or home office, our platform connects you with leading UPS suppliers to ensure uninterrupted power, data protection, and peace of mind.
Still have questions? Contact our UPS experts for personalized recommendations, sizing assistance, or a free quote tailored to your unique requirements.









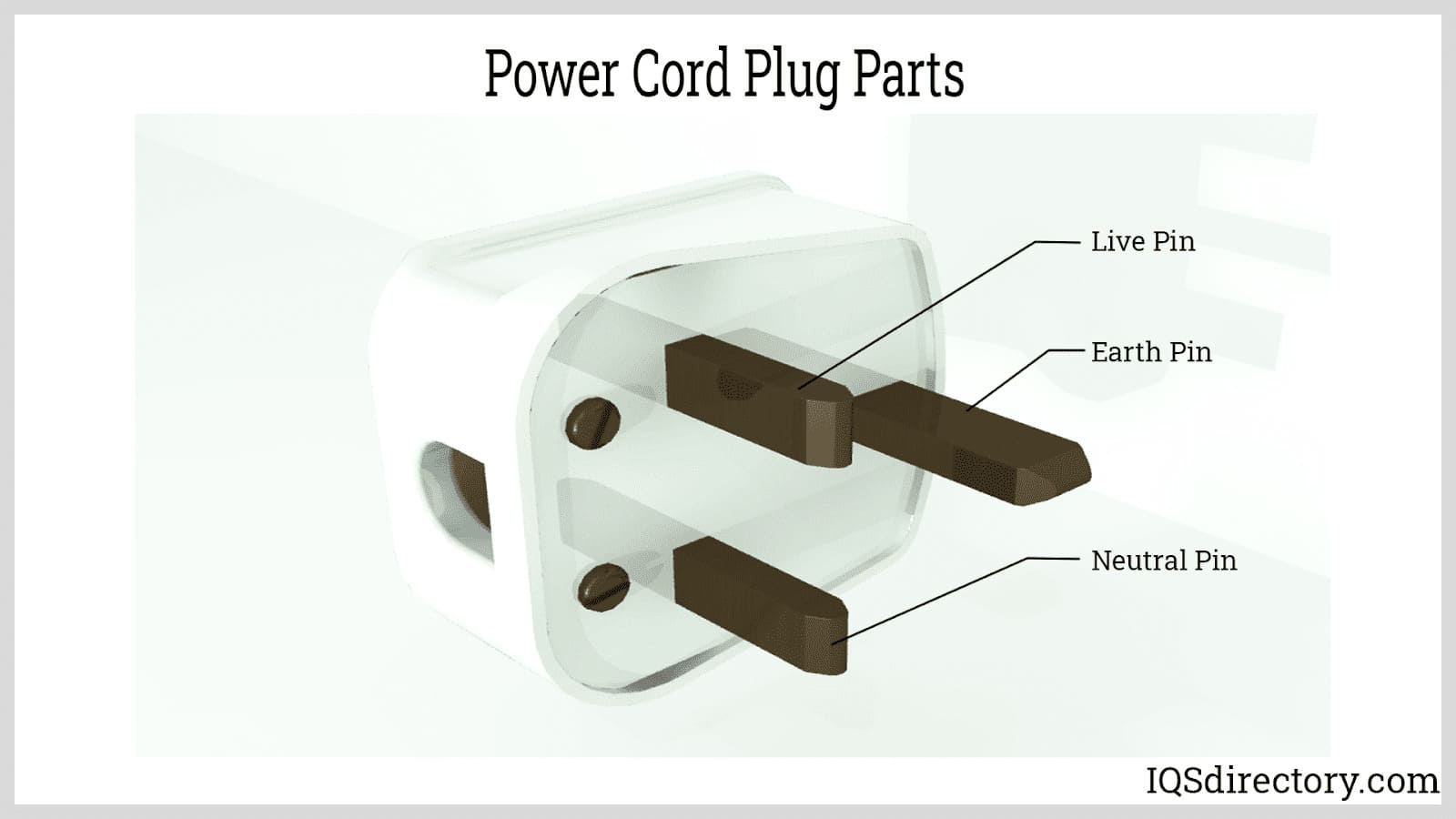

 Electric Coils
Electric Coils Electric Switches
Electric Switches Electric Transformers
Electric Transformers Electronic Connectors
Electronic Connectors Electronic Enclosures
Electronic Enclosures Membrane Switches
Membrane Switches Power Cords
Power Cords Power Supplies
Power Supplies Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services